Введение
The hematology analyzer market stands at a critical inflection point. Valued at approximately USD 4.33 billion in 2025, the global market for blood diagnostic equipment is projected to reach USD 7.28 billion by 2034, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 5.97%. This explosive growth underscores a fundamental truth in modern healthcare: accurate, rapid blood diagnostics are no longer a convenience—they are essential infrastructure for clinical decision-making across all healthcare settings.
When healthcare administrators and laboratory directors evaluate the decision to buy a hematology analyzer, they face a landscape transformed by artificial intelligence, complete blood morphology analysis, and point-of-care democratization. The traditional paradigm—where advanced diagnostics existed exclusively within hospital reference laboratories—has given way to a new reality where compact, intelligent analyzers deliver pathologist-level diagnostic capability directly to emergency departments, community clinics, ambulances, and primary care facilities.
The Complete Blood Count (CBC) remains the most frequently ordered laboratory test in clinical practice worldwide, informing approximately 70% of clinical decisions in healthcare settings. Yet the quality, speed, and interpretive depth of CBC results vary dramatically depending on the technology platform selected. Understanding the landscape of modern hematology analyzers—their technological foundations, clinical applications, operational characteristics, and comparative advantages—enables informed procurement decisions that align with institutional diagnostic needs and long-term strategic positioning.
The Evolution of Blood Diagnostics: From Manual Microscopy to AI-Powered Analysis
Historical Progression and Current State
Blood cell counting and analysis has undergone radical transformation over the past 170 years. The timeline traces from manual hemocytometer methods introduced in 1852, through impedance-based automated counters developed in the 1970s, to flow cytometry systems emerging in the 1980s and 1990s, and finally to artificial intelligence-enhanced cell morphology analysis beginning in 2017.
Each technological generation improved efficiency and consistency, yet each also inherited limitations from its predecessors. Impedance-based analyzers count cells by electrical pulse magnitude—a methodology fundamentally blind to morphology, unable to distinguish between normal cells and pathologic variants. Flow cytometry systems added dimensional sophistication through laser-based detection but require complex reagent systems, maintenance protocols, and operational expertise. Traditional manual blood smear microscopy—the historical gold standard for cell morphology assessment—remains dependent on individual technician expertise, training levels, and subjective interpretation frameworks that vary widely between institutions.
The most recent paradigm shift centers on artificial intelligence applied to complete blood morphology (CBM). Rather than abandoning morphological assessment (as impedance systems did) or requiring expert operator interpretation (as microscopy does), AI-powered systems automate the cognitive work of pathologists while preserving the diagnostic depth of morphologic analysis.
What Changed: The AI Advantage
Modern AI hematology analyzers employ a fundamentally different diagnostic architecture than their predecessors. Instead of mathematical inference from electrical or optical measurements, these systems capture high-resolution digital microscopic images of individual blood cells, then apply deep learning algorithms to recognize cellular characteristics with pathologist-level accuracy.
Ozelle’s proprietary algorithm, trained on 40 million real patient samples and recognized at the 2022 World Artificial Intelligence Conference, exemplifies this transformation. The system’s “Expert Brain” combines:
Precision Eyes: SwissOptic customized lens technology capturing images at 4-megapixel resolution with 50 frames-per-second acquisition
Advanced Optical Imaging: High-resolution imaging at oil-immersion equivalence capturing cellular architecture with sub-micrometer precision
Deep Learning Recognition: Convolutional neural networks identifying 37+ blood cell parameters and abnormal morphologies
Automated Mechanical Precision: Robotic positioning systems maintaining 1-micrometer accuracy across thousands of analyses
The clinical difference is profound. While traditional impedance analyzers struggle with severe anemia, extreme leukocytosis, or malignant cell populations—situations where electrical properties diverge from biological reality—AI morphology systems maintain accuracy across the full pathologic spectrum. A septic patient with left-shifted neutrophils (immature neutrophil predominance), a leukemia patient with circulating blasts, or an anemic patient with fragmented red cells receives accurate analysis instead of potential diagnostic errors.
Understanding Hematology Analyzer Technology: Core Methodologies and Differentiation
Technology-Based Market Segmentation
The hematology analyzer market segments into distinct technology categories, each with specific clinical strengths, operational implications, and cost profiles:
Flow Cytometry-Based Systems (46% market share, 2024): These advanced platforms utilize laser-based detection to identify and classify cells based on size, internal complexity, and fluorescent properties. Flow cytometry offers superior diagnostic depth and is particularly valued in hematology-oncology units and reference laboratories where detecting abnormal populations justifies premium pricing. These systems typically require skilled operators, complex reagent management, and regular maintenance protocols.
Impedance-Based Systems (Declining segment): Traditional electrical impedance counting—where cells generate voltage pulses proportional to size—remains prevalent in basic laboratory settings but increasingly faces displacement by morphology-based approaches. These systems lack morphologic recognition capability and generate high rates of manual review flags in abnormal populations.
AI-Enhanced Cell Morphology Systems (Emerging growth leader): The newest category combines automated microscopy with deep learning algorithms. These systems capture high-resolution images, apply artificial intelligence for cell classification, and maintain laboratory-equivalent accuracy while reducing operator burden. This segment is experiencing the most rapid adoption, particularly in distributed diagnostics and mid-market laboratory upgrades.
The Complete Blood Morphology (CBM) Advantage
Complete Blood Morphology represents a synthesis of traditional morphologic analysis with modern automation and AI interpretation. Rather than operator-dependent manual slide review or algorithm-dependent impedance counting, CBM systems capture detailed cellular images and apply trained neural networks to recognize cell types, sizes, shapes, and abnormalities.
The clinical granularity this enables is substantial. Traditional CBC analysis reports parameters such as WBC, RBC, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and basic leukocyte differential (neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils). Advanced CBM systems report these same parameters plus sophisticated abnormality detection:
- NST, NSG, NSH: Neutrophil maturation stages indicating bone marrow response intensity
- RET: Reticulocyte counts revealing bone marrow productivity and red cell recovery
- PAg: Platelet aggregates indicating platelet function and clotting capacity
- ALY: Atypical lymphocytes suggesting viral infection or immune activation
- Morphologic abnormalities: Schistocytes (fragmented cells), echinocytes (spiculated cells), teardrop cells, and other forms indicating specific pathologies
This morphologic information bridges the diagnostic gap between basic cell counting and clinical decision-making. A patient presenting with fever, hypotension, and suspected sepsis receives not only elevated WBC count but also NST elevation indicating immature neutrophil predominance—objective confirmation of severe infection. A patient with hemolytic anemia receives not only low hemoglobin and elevated reticulocyte count but also schistocyte detection confirming mechanical hemolysis.
Clinical Applications and Diagnostic Value Across Healthcare Settings
Emergency Department and Critical Care
The emergency department represents perhaps the highest-value application for advanced hematology analyzers. When a septic patient arrives with fever, hypotension, and altered mental status, every minute of diagnostic delay increases mortality risk. Rapid, accurate CBC results with abnormality flagging enable immediate clinical decision-making:
Elevated WBC (>11,000), immature neutrophil flagging (NST >5%), and left shift patterns provide objective sepsis confirmation. Paramedics and emergency physicians can initiate broad-spectrum antibiotics based on laboratory findings rather than clinical judgment alone, reducing door-to-antibiotic time from typical 45 minutes to under 15 minutes—a transformation that directly improves sepsis survival.
For trauma patients with acute hemorrhage, immediate hemoglobin and platelet values guide transfusion decisions and volume resuscitation strategies. For patients with acute dyspnea, rapid CBC helps differentiate infection from other etiologies. For patients with altered mental status, CBC abnormalities point toward specific diagnoses (sepsis, bleeding, leukemia) guiding focused evaluation.
Intensive Care Unit Monitoring
Critically ill ICU patients require longitudinal CBC trending—not single-point measurements but sequential values detecting trends days before clinical deterioration becomes obvious. Real-time trending of platelet counts identifies developing thrombocytopenia (predicting bleeding risk or signaling DIC development). Rapid WBC differential changes detect infection development hours before clinical signs appear. Hemoglobin monitoring guides transfusion decisions with evidence-based precision.
The operational difference is substantial. With traditional analyzer turnaround times of 30-60 minutes, ICU teams make decisions based on hours-old data. With AI morphology systems delivering results within 6 minutes, clinicians possess information reflecting current patient physiology.
Hospital Laboratories and High-Volume Diagnostic Centers
Clinical laboratories processing 100+ samples daily benefit from automation that maintains quality while scaling throughput. AI morphology analyzers process 10-12 samples per hour without sacrificing diagnostic depth. More importantly, reduced manual slide review (through preliminary AI assessment) preserves highly skilled technician capacity for genuinely abnormal findings requiring human expertise.
The economic model shifts favorably. Rather than hiring additional technicians to maintain volume, laboratories maintain or increase throughput with existing staffing. Maintenance-free operation (no regular service calls, no pipeline design complexity) reduces operational costs. Comprehensive results (including morphology data) reduce callbacks and repeat testing.
Первичная помощь и общественные медицинские центры
The point-of-care hematology diagnostics market, valued at USD 2.4 billion in 2023, is projected to reach USD 3.6 billion by 2030—growing faster than centralized laboratory segments. This reflects fundamental healthcare delivery transformation: patients increasingly receive diagnostics and treatment in primary care settings rather than hospital referral laboratories.
Compact, maintenance-free analyzers like Ozelle’s EHBT-25 and EHBT-50 enable small clinics and community health centers to offer same-visit diagnosis and treatment initiation. A patient presenting with fatigue receives hemoglobin analysis and anemia diagnosis immediately. A patient with fever receives leukocyte analysis confirming bacterial infection, enabling antibiotic initiation same-visit. A patient with bleeding concerns receives platelet analysis within minutes.
This democratization of diagnostic capability directly improves health equity. Rural communities, underserved urban neighborhoods, and primary care settings no longer require specialized laboratory infrastructure or turnaround delays that previously limited diagnostic capability to hospital environments.
Hematology-Oncology and Cancer Monitoring
Oncology represents a specialized application where advanced hematology analysis delivers distinct clinical value. Cancer patients receiving chemotherapy or immunotherapy require frequent CBC monitoring for treatment tolerance, circulating malignant cell detection, and treatment complication identification.
AI morphology systems excel in this environment through:
- Early malignant cell detection: Circulating blasts in leukemia patients without manual pathology review requirement
- Treatment complication monitoring: Febrile neutropenia (infection-causing low WBC), thrombocytopenia (bleeding risk), and anemia from treatment
- Leukemia subclassification: Blast morphology guiding targeted therapy selection
- Treatment response assessment: Declining blast populations indicating therapy effectiveness
Traditional flow cytometry systems require reference laboratory centralization, creating turnaround delays incompatible with treatment decision-making. AI morphology systems provide preliminary classification within minutes, with capability for expert review of complex cases.
Operational Advantages: Maintenance, Sample Volume, and Cost Economics
Maintenance-Free Operation and Simplified Workflows
Traditional hematology analyzers employ complex reagent pipelines, dilution systems, and washing mechanisms requiring regular maintenance, recalibration, and technician expertise. System downtime from maintenance or malfunction—sometimes weeks—disrupts laboratory operations and creates diagnostic backlogs.
Modern AI morphology analyzers from Ozelle employ individual test cartridges (single-use disposable units) rather than pipeline designs. Each test employs its own reagent kit, eliminating cross-contamination risks, blockages, and maintenance requirements. The system operates maintenance-free, with reagent kits stored at room temperature requiring no special infrastructure.
The operational impact is substantial. A small clinic deploying an EHBT-25 analyzer requires no specialist technician for maintenance, no cold-chain logistics for reagents, and no downtime from service calls. The device operates reliably for years with consumable replacement being the only user-initiated activity.
Sample Volume and Throughput Optimization
Clinical throughput requirements span an enormous range—from small clinics processing 5-10 samples daily to reference laboratories processing 500+ samples daily. The hematology analyzer market accommodates this range through tiered product portfolios:
Compact POC Analyzers (EHBT-25): Processing 12 samples per hour, suitable for clinics and small facilities with minimal sample volumes
Mid-Tier Multi-Functional Analyzers (EHBT-50): Processing 10 samples per hour with expanded test menu (hematology, immunoassay, biochemistry, urine analysis), designed for primary care centers and clinics seeking consolidated diagnostics
High-Throughput Analyzers (EHBT-75): Processing up to 10 samples per hour with advanced abnormality detection
Veterinary Applications (EHVT-50, EHVT-75): Specialized analyzers for veterinary diagnostics supporting blood, urine, and fecal analysis in animal healthcare
This modular approach enables facilities to select analyzers matching their actual workload rather than over-purchasing capacity or under-purchasing, creating diagnostic bottlenecks.
Economic Considerations: Capital, Operational, and Result-Value Costs
When healthcare administrators evaluate hematology analyzer procurement, the financial decision encompasses multiple dimensions beyond initial equipment cost:
Capital Investment: Equipment purchase price varies dramatically by technology type and throughput capacity. Basic impedance counters remain affordable; advanced AI morphology systems command premium pricing reflecting sophisticated technology. Cost-per-sample calculations, however, often favor advanced systems through reduced labor requirements and maintenance-free operation.
Operational Costs: Maintenance expenses, quality control reagent costs, technician training requirements, and system downtime impact total cost of ownership. Maintenance-free analyzers with room-temperature storage and individual test kits reduce operational complexity.
Result Value: The diagnostic depth and clinical actionability of results drives the true value proposition. A basic analyzer generating simple cell counts may require manual microscopy review for abnormal cases, consuming technician time and delaying results. An AI morphology analyzer providing comprehensive cell classification, abnormality detection, and AI interpretation support reduces manual review requirements and accelerates clinical decision-making.
Healthcare systems calculating return on investment should consider not only equipment and reagent costs but also labor savings, diagnostic turnaround acceleration, and clinical outcome improvements from earlier diagnosis and treatment initiation. From this perspective, premium-category AI morphology analyzers often deliver superior economic value despite higher initial capital investment.
Comparative Technology Analysis: Ozelle Solutions in the Competitive Landscape
Product Portfolio Overview
Ozelle’s hematology analyzer family spans from entry-level to advanced multi-functional platforms, each addressing distinct market segments and clinical applications:
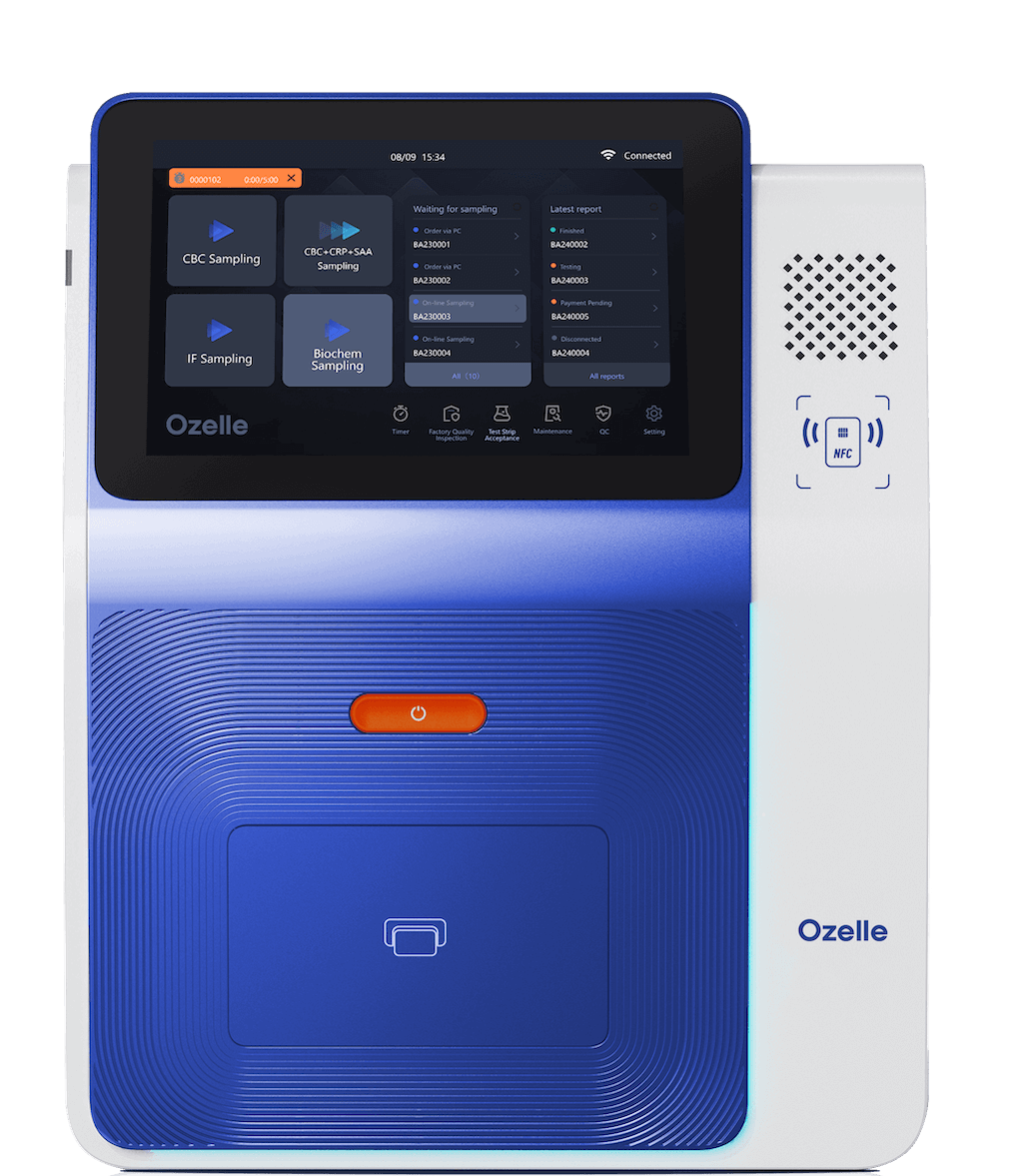
EHBT-25: Entry-level 3-diff cell morphology analyzer providing foundational CBC analysis with AI-enhanced accuracy. Compact dimensions (360mm × 290mm × 400mm), 8.1kg weight, and 12 samples-per-hour throughput suit small clinics and community health centers. Processing capillary or venous blood samples of 40µL, delivering results in 6 minutes with maintenance-free operation.
EHBT-50 Mini Lab: The mid-tier all-in-one platform combining 7-diff hematology analysis with immunoassay, biochemistry, urine, and fecal testing. Processing 10 samples per hour with 30µL capillary blood requirements, the EHBT-50 consolidates multiple diagnostic functions into single equipment, optimizing laboratory space and reducing procedural complexity. 10.1-inch touch screen, built-in thermal printer, and WiFi/Ethernet connectivity enable seamless integration with hospital information systems.
EHBT-75: Advanced 7-diff analyzer with enhanced abnormality detection including NST, NSG, NSH, NLR, PLR, ALY, PAg, and RET. Single-use cartridge technology with 6-minute result delivery, liquid-based cytology staining, and high-resolution morphology imaging. Designed for hospital laboratories requiring sophisticated abnormality detection without maintenance burden.
EHVT-50 and EHVT-75: Veterinary-specific multi-functional analyzers supporting blood, urine, fecal, and immunoassay analysis in veterinary clinics and animal healthcare facilities.
Competitive Positioning Within Market Landscape
The global hematology analyzer market includes established high-volume manufacturers (Sysmex, Beckman Coulter, HORIBA) alongside emerging innovators introducing AI-powered approaches. Ozelle’s competitive positioning reflects several distinct advantages:
AI-Powered Morphology at Scale: With 50,000 units installed worldwide providing diagnostics to 40 million patients, Ozelle has demonstrated market validation of AI morphology technology. The 2022 WAIC recognition of the algorithm underscores technological sophistication.
Maintenance-Free Operation: While traditional analyzers require regular service and expertise, Ozelle systems operate with individual cartridge designs eliminating pipeline complexity.
Modular Product Portfolio: Rather than forcing all customers into single product category, Ozelle offers EHBT-25, EHBT-50, EHBT-75, and veterinary variants enabling right-sizing to facility-specific needs.
Multi-Functional Integration: The EHBT-50 consolidates hematology, immunoassay, biochemistry, and additional testing, reducing equipment footprint and operational complexity compared to multi-instrument laboratories.
Global Regulatory Approvals: CE, FDA, ISO 13485, CQC, and related certifications enable deployment across developed and emerging markets.
Point-of-Care Accessibility: Compact dimensions, maintenance-free operation, and room-temperature reagent storage enable deployment in emergency departments, ambulances, primary care clinics, and mobile units previously limited to basic testing.
Market Dynamics and Procurement Considerations
Regional Adoption Patterns and Healthcare Infrastructure
The hematology analyzer market exhibits pronounced geographic segmentation reflecting healthcare infrastructure maturity and economic development:
North America (41% market share): Mature healthcare infrastructure with universal analyzer deployment, robust reimbursement mechanisms supporting premium technology adoption, and established relationships between laboratory systems and equipment manufacturers. Premium analyzer pricing is supported by healthcare spending levels and reimbursement policies.
Europe: Strong regulatory frameworks (CE marking), established laboratory standards, and technology leadership in diagnostics. European adoption emphasizes quality assurance and clinical validation.
Asia-Pacific (Fastest-growing region): Rapidly improving healthcare infrastructure in China, India, Vietnam, and Indonesia; government investments in diagnostic laboratory development; rising prevalence of blood disorders in aging populations; and emerging manufacturer growth capitalizing on infrastructure modernization. Growth rates in Asia-Pacific exceed North America and Europe, creating substantial market opportunities for appropriately positioned manufacturers.
Healthcare administrators purchasing analyzers should consider geographic expansion plans. Equipment selected should maintain supportive regulatory status and manufacturer presence across relevant regions. Ozelle’s multi-region presence (Silicon Valley R&D, German headquarters, global manufacturing) supports this consideration.
Clinical Requirements Analysis and Needs Assessment
Prudent hematology analyzer procurement follows systematic needs assessment addressing facility-specific requirements:
Case Volume and Throughput Requirements: Calculate expected daily sample volume across all patient categories. Small clinics may operate at 5-15 samples daily; mid-sized laboratories at 50-150 daily; reference laboratories at 300-500+ daily. Analyzer throughput capacity should match anticipated volume with 20-30% buffer for growth.
Test Menu Requirements: Evaluate whether facilities require basic CBC analysis or expanded testing (immunoassay, biochemistry, urine, fecal analysis). Multi-functional analyzers like the EHBT-50 consolidate testing but may exceed requirements for single-purpose clinics.
Operator Expertise Available: Maintenance-free, user-friendly systems suit facilities with minimal laboratory staff. Complex analyzers requiring regular maintenance suit high-volume laboratories with dedicated technical staff.
Connectivity and Data Integration Needs: Hospital systems requiring LIS (Laboratory Information System) integration need analyzers supporting standard interfaces (LIS, HIS, Ethernet, USB). Standalone clinics may prioritize built-in reporting capability over network connectivity.
Physical Space Constraints: Compact analyzers suit space-limited clinics (EHBT-25: 360×290×400mm, 8.1kg). Multi-functional platforms suit larger laboratories seeking to consolidate equipment footprint.
Budget Constraints: Equipment costs vary substantially. Needs assessment should balance performance requirements against financial reality. TCO (total cost of ownership) calculations including equipment, reagents, maintenance, training, and labor should guide investment decisions.
The Future of Hematology Diagnostics: Technology Trajectories and Market Evolution
Artificial Intelligence Integration and Diagnostic Evolution
The trajectory of AI in hematology diagnostics reflects three distinct technological phases with different clinical and economic implications:
Phase 1 (2025-2027) – Current State: AI morphology transitions from premium differentiation toward industry standard. Regulatory frameworks standardizing AI-assisted diagnostics emerge globally. Market consolidation accelerates among established players with continued acquisition activity.
Phase 2 (2028-2031) – Distributed Diagnostics Acceleration: Migration toward point-of-care analyzers intensifies as compact, maintenance-free systems achieve laboratory-equivalent accuracy. Tiered pricing models expand access to emerging markets. AI diagnostics increasingly become table-stakes rather than competitive differentiators.
Phase 3 (2032-2035) – Integrated Healthcare Ecosystems: Connected intelligence through IoT-enabled platforms enables population-level diagnostics, epidemiologic trend detection, and machine learning model optimization at scale. Integration with other diagnostic modalities (imaging, genomics, biomarkers) creates comprehensive patient phenotyping supporting precision medicine.
For facilities making current procurement decisions, understanding this trajectory is important. Equipment selected today should support integration with evolving AI capabilities and connected platforms anticipated for the coming decade.
Emerging Application Domains
Beyond traditional hematology-oncology and infection diagnostics, emerging applications drive market expansion:
Sepsis Detection and Risk Stratification: AI algorithms integrating CBC parameters with clinical context generate sepsis risk scores and alert systems, assisting early recognition and intervention.
Malaria and Parasitic Infection Detection: AI analysis of blood smears achieves >95% accuracy in malaria diagnosis—crucial in endemic regions where early detection improves outcomes.
Rare Disease Diagnosis: AI morphology systems excel at identifying rare cell populations and morphologic variants suggesting specific diagnoses previously requiring expert pathology review.
Treatment Monitoring and Personalized Medicine: Longitudinal CBC trending combined with AI interpretation supports treatment optimization and adverse event prediction in cancer, immunotherapy, and chronic disease management.
These emerging applications suggest that hematology analyzers will evolve from standalone diagnostic devices toward integrated platforms supporting comprehensive clinical decision-making and precision medicine approaches.
Conclusion: Strategic Procurement Framework for Modern Hematology Analyzers
The decision to buy a hematology analyzer represents more than equipment procurement—it reflects institutional commitment to diagnostic capability, operational efficiency, and patient outcome improvement. As the global hematology analyzer market expands from USD 4.33 billion (2025) to USD 7.28 billion (2034), the competitive landscape increasingly fragments around technological differentiation, operational simplicity, and clinical validation.
Healthcare administrators evaluating analyzer options should consider multiple dimensions: technological foundation (AI morphology versus traditional impedance/flow cytometry), operational requirements (maintenance burden, throughput capacity, sample volume), clinical needs (test menu comprehensiveness, abnormality detection capability), and strategic considerations (connectivity, future-readiness, regulatory status).
Ozelle’s portfolio of AI-powered hematology analyzers—from the entry-level EHBT-25 through the advanced EHBT-50 and EHBT-75 platforms—addresses diverse facility requirements while maintaining consistent technological sophistication grounded in 40 million sample training datasets and 50,000 units of global deployment. The maintenance-free operation, room-temperature reagent storage, and modular design enable deployment across healthcare settings from ambulances to hospital reference laboratories.
The future of hematology diagnostics belongs to manufacturers combining clinical innovation through AI-powered morphology analysis, operational simplicity through maintenance-free design, global accessibility through tiered product portfolios, and connected intelligence through IoT-enabled platforms. For healthcare systems prioritizing diagnostic accuracy, operational efficiency, and cost containment, comprehensive evaluation of both established market leaders and innovative emerging manufacturers ensures optimal alignment between technology selection and long-term strategic objectives.
Learn more about Ozelle’s complete hematology analyzer portfolio, technical specifications, and clinical applications by visiting https://ozellemed.com/en/