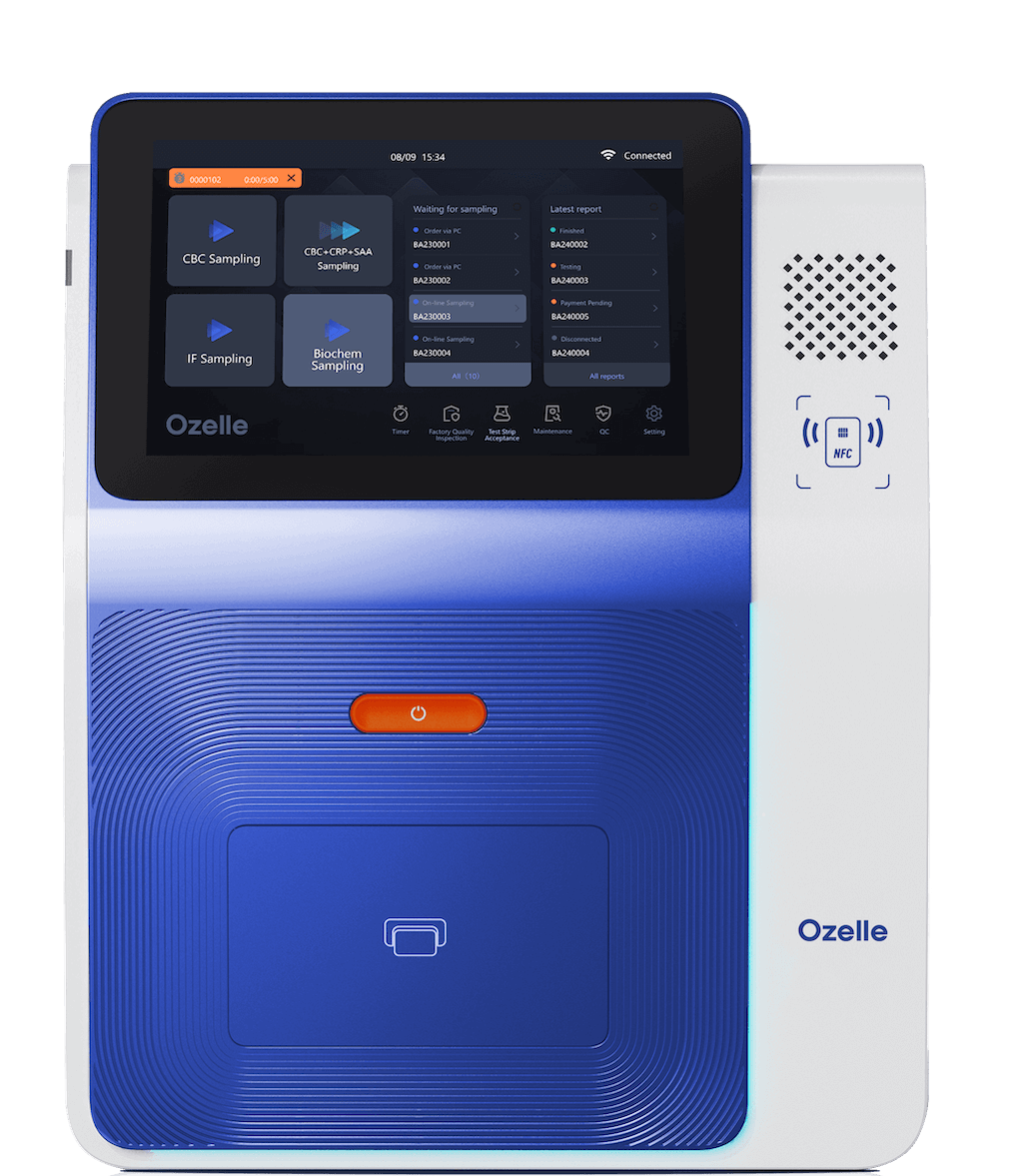
Healthcare facilities across the globe face a critical decision when selecting point-of-care (POC) blood analyzers. The market offers numerous options, each with distinct capabilities, pricing models, and operational requirements. This procurement choice directly impacts laboratory efficiency, patient outcomes, and overall healthcare costs, yet many decision-makers struggle to navigate the technical complexities and feature differentiation between available devices.
The challenge is multifaceted. Healthcare administrators must weigh automation capabilities against physical space constraints, evaluate throughput requirements against actual patient volume, and justify capital investments through demonstrated cost savings and clinical utility. Without a clear framework for comparison, facilities risk investing in technology that doesn’t align with their specific needs—resulting in underutilization, workflow inefficiencies, and missed opportunities for improved patient care.
This comprehensive guide clarifies the key differences between POC analyzer tiers, providing structured comparison frameworks to match device capabilities with facility requirements. By understanding the fundamental distinctions between dedicated hematology platforms and multi-functional systems, healthcare leaders can make informed procurement decisions that optimize both clinical performance and operational economics.
Understanding POC Blood Analyzer Fundamentals
What Is a POC Blood Analyzer?
Point-of-care blood analyzers represent a fundamental shift in diagnostic testing delivery. These automated hematology devices provide laboratory-grade complete blood count (CBC) results in just 6 to 10 minutes—a dramatic improvement over traditional central laboratory workflows that typically require 2-6 hours for routine reporting”24 to 48 hours for result reporting.
The speed advantage translates directly into clinical value. Clinicians receive actionable diagnostic information in real time, enabling immediate clinical decisions for patient treatment and management. This rapid turnaround proves particularly critical in emergency departments, acute care settings, and high-volume screening environments where time-sensitive decisions directly impact patient outcomes.
Instead of relying on centralized laboratories and multi-step logistics, POC systems keep the sample at the patient site, fundamentally restructuring the diagnostic workflow. By removing transportation, batching, and manual hand-off steps—which together account for nearly 70% of the turnaround time in traditional pathways—these analyzers eliminate the largest sources of delay and variability in routine hematology testing.
POC Blood Analyzer Core Technology
Modern POC blood analyzers leverage sophisticated technological innovations that drive their clinical performance. AI-powered cell recognition and classification algorithms analyze cellular morphology approaching the level of expert pathologists. These deep learning systems identify not only standard white blood cell types but also detect abnormal cells and immature cell forms that might escape traditional counting methods.
The technology relies on liquid-based staining with high-resolution imaging, capturing detailed cellular structures in vibrant color dimensions. Fully automated sample processing handles loading, staining, and mixing operations without manual intervention, reducing opportunities for operator error and ensuring consistent results across different users and shifts.
The accuracy metrics demonstrate exceptional performance. Lab-grade correlation coefficients reach ≥0.99 across critical parameters—with white blood cell (WBC) correlation at 0.9962, red blood cell (RBC) at 0.9787, hemoglobin (HGB) at 0.9867, and platelets (PLT) at 0.9834. These performance standards match or exceed results from leading international laboratory analyzers.
POC Blood Analyzer Key Features
POC blood analyzers share several defining characteristics that position them as practical solutions for decentralized diagnostics:
7-Differential CBC with abnormal cell detection represents the core analytical capability. Beyond traditional five-part differentials (neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils), modern POC systems identify advanced parameters including immature neutrophils (NST), nucleated red blood cells (NRBCs), and reticulocytes (RET), providing richer clinical context for hematologic assessment.
Single-use cartridges stored at room temperature eliminate the maintenance burden that traditionally associated with laboratory analyzers. No daily calibration, no complex quality control procedures, no risk of cross-contamination or mechanical blockages. This maintenance-free design dramatically reduces operational complexity and associated costs.
Minimal sample volume requirements—just 30 microliter (μL) capillary or venous blood—enable convenient testing without the trauma of traditional venipuncture. This proves especially valuable for pediatric and geriatric populations where repeated blood draws create compliance challenges and patient discomfort.
Comparing Analyzer Tiers: EHBT-50 vs. EHBT-75
Healthcare facilities selecting POC analyzers typically encounter two primary platform categories: multi-functional systems designed for comprehensive laboratory consolidation, and dedicated hematology devices optimized for high-volume screening. The Ozelle product line exemplifies this tier differentiation through the EHBT-50 and EHBT-75 platforms.
| Caratteristica | EHBT-50 | EHBT-75 |
| Primary Use | Multi-functional diagnostics | Dedicated hematology |
| Test Modules | CBC + Immunoassay + Biochemistry + Urine/Fecal | Solo CBC |
| 7-Diff Parameters | 37 parameters | 37 parameters |
| Produttività | 10 campioni/ora | 10 campioni/ora |
| Risultato Tempo | 6-10 minuti | 6 minuti |
| Dimensioni | 350 × 400 × 450 mm (standard) | 415 × 203 × 483 mm (compact) |
| Power Consumption | Standard | Lower (48VA) |
| Best For | Lab consolidation | High-volume CBC screening |
| Price Tier | Higher | Lower |
EHBT-50: Multi-Functional Mini Lab Platform
The EHBT-50 represents a paradigm shift in point-of-care diagnostics through complete laboratory consolidation. Rather than deploying separate devices for hematology, immunoassay, and biochemistry testing, this platform combines all testing modalities into a single, space-efficient instrument.
The device delivers comprehensive diagnostic capabilities spanning multiple clinical domains. The hematology module provides the full 37-parameter CBC with advanced differential detection. Immunoassay functionality enables cardiac marker measurement (NT-ProBNP, cardiac troponin I, myoglobin), inflammation assessment (CRP, SAA, IL-6, PCT), and hormone analysis. Biochemistry testing covers glucose and lipid profiles, renal and liver function assessment, and bone metabolism markers like 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Additional modules support urine and fecal analysis, with expandable test menus available through over-the-air (OTA) software updates.
This all-in-one versatility proves transformative for multi-specialty clinics and comprehensive diagnostic laboratories. Rather than coordinating results from multiple instruments or managing sample routing to different testing platforms, clinicians receive consolidated results from a single device. The workflow efficiency gains translate directly into faster diagnostic turnaround and reduced operational overhead.
The EHBT-50 particularly excels in laboratory consolidation scenarios. Facilities can eliminate 3-4 separate devices, recover significant laboratory space, and reduce staffing requirements for instrument maintenance and troubleshooting. The standardized interface and integrated LIS/HIS connectivity streamline workflow integration across departments.
EHBT-75: Dedicated Hematology Platform
The EHBT-75 optimizes for focused clinical excellence in complete blood count analysis. This dedicated hematology platform delivers the same sophisticated 7-differential CBC with 37 parameters as its multi-functional counterpart, but eliminates the complexity associated with additional test modules.
The compact footprint—415 × 203 × 483 mm—enables deployment in physical spaces that would challenge larger analyzers. Emergency departments with space constraints, mobile health units, pharmacy corners, and ambulances all represent ideal deployment scenarios. The minimal power consumption (48VA) further facilitates deployment in resource-limited environments where power infrastructure may be constrained.
The focused design philosophy delivers profound advantages for high-volume hematology screening environments. With 10 samples per hour throughput delivering 6-minute result times, the EHBT-75 enables rapid patient assessment without the complexity of managing additional test modules. Lower capital costs compared to multi-functional platforms improve procurement accessibility for smaller facilities and rural healthcare settings.
The device proves particularly valuable in specialized clinical environments. Dedicated hematology/oncology units benefit from concentrated focus on morphologic assessment and abnormal cell detection. Emergency departments managing sepsis protocols appreciate the rapid CBC turnaround enabling quick antimicrobial escalation decisions. Primary care practices serving pediatric populations leverage capillary sampling to eliminate venipuncture discomfort.
POC Blood Analyzer Key Decision Factors
Selecting the appropriate POC analyzer requires systematic evaluation across multiple dimensions. Healthcare facilities should assess their unique requirements across patient volume, testing scope, physical infrastructure, financial constraints, and workflow integration considerations.
Patient Volume and Throughput Requirements
Patient volume fundamentally shapes analyzer selection strategy. Low-volume settings seeing 1-5 patients daily can utilize either platform based primarily on testing needs, as throughput capacity exceeds typical case volume. The EHBT-75’s lower cost and simpler operation may prove advantageous unless comprehensive testing drives the clinical decision.
Medium-volume facilities managing 10-30 patients daily benefit from EHBT-50 multi-functional consolidation. The ability to perform comprehensive testing—combining CBC, cardiac markers, inflammation panels, and metabolic assessment—improves diagnostic clarity while streamlining sample management and result reporting.
High-volume environments exceeding 50 patients daily warrant strategic dual deployment. Facilities might deploy EHBT-50 as the primary platform for comprehensive testing while strategically positioning EHBT-75 units in distributed locations (emergency departments, urgent care areas, pharmacy) to capture high-volume CBC screening and distribute testing load.
Testing Scope Assessment
CBC-only requirements clearly favor EHBT-75 deployment. Facilities that primarily require rapid hematologic assessment without need for immunoassay, biochemistry, or urine testing gain maximum cost efficiency and operational simplicity through dedicated hematology platforms.
Comprehensive diagnostic requirements justify EHBT-50 selection. Multi-specialty clinics managing infection workup (requiring CBC + immunoassay + biochemistry), diabetes management (requiring glucose + HbA1c assessment), and kidney disease surveillance (requiring CBC + creatinine + kidney biomarkers) achieve superior efficiency through consolidated testing on a single platform.
Specialized applications warrant situational deployment. Oncology units benefit from dedicated EHBT-75 devices for morphologic assessment and abnormal cell detection. Community health centers serving diverse populations gain maximum value from EHBT-50 comprehensive capabilities.
Physical Space and Infrastructure
The EHBT-75’s compact design (415 × 203 × 483 mm) opens deployment opportunities unavailable for standard laboratory instrumentation. Emergency departments operating under space constraints, mobile health units and ambulances requiring portable equipment, and pharmacy corners seeking POC integration all benefit from this compact footprint.
The EHBT-50 maintains a standard laboratory footprint (350 × 400 × 450 mm), requiring dedicated countertop space within laboratory areas. Larger facilities with dedicated laboratory infrastructure absorb this space requirement easily. Smaller facilities should assess available space carefully before commitment.
Both platforms integrate seamlessly with existing healthcare information systems. WiFi/Ethernet connectivity enables LIS/HIS integration across distributed locations. Power requirements remain modest—EHBT-75 operates at just 48VA, enabling deployment in resource-limited environments, while EHBT-50 standard power consumption remains reasonable for typical laboratory settings.
Budget Considerations
Capital cost represents a significant consideration in analyzer selection. EHBT-75 lower initial procurement cost reduces financial barriers for smaller facilities, primary care clinics, and resource-limited settings. Lower ongoing power consumption (48VA vs. standard consumption) translates into measurable utility cost savings over the device lifecycle.
EHBT-50 higher initial investment finds justification through operating cost reduction. Laboratory consolidation eliminating 3-4 separate devices generates space recovery, reduced staffing requirements, and simplified maintenance protocols. The ability to perform comprehensive testing in-house eliminates reference laboratory send-outs, generating cost savings that typically justify the higher initial investment within 12-24 months.
Both platforms eliminate the frequent maintenance and bulk reagent deterioration costs associated with traditional laboratory analyzers. Single-use cartridge systems stored at room temperature prevent reagent degradation and cross-contamination risks, dramatically reducing reagent waste and quality control failures compared to traditional systems requiring daily maintenance and validation.
Workflow Integration and User Experience
Modern POC analyzers prioritize user accessibility through intuitive interface design. Both EHBT-50 and EHBT-75 feature touchscreen displays enabling rapid user training. Nurses, phlebotomists, and clinicians with minimal laboratory experience can operate devices confidently after brief orientation.
Capillary sampling capability transforms workflow dynamics by eliminating venipuncture requirements for POC deployment. Fingerstick sampling reduces patient discomfort, eliminates phlebotomy scheduling delays, and enables rapid point-of-service testing in emergency departments, urgent care areas, and primary care clinics.
Result turnaround transformation represents perhaps the most significant workflow impact. Traditional central laboratory testing requiring 24-48 hours shifts to same-day diagnostic decision-making. This acceleration proves particularly critical for acute presentations where diagnostic uncertainty delays therapeutic intervention. Sepsis cases, acute anemia assessment, and infection typing all benefit from rapid POC turnaround enabling immediate clinical action.
Real-World Facility Matching of POC Blood Analyzer
The theoretical frameworks outlined above find practical expression through facility-specific deployment scenarios. Understanding how different facility types align with analyzer platform capabilities enables procurement decisions that deliver maximum clinical and operational value.
Primary Care Clinic (5-10 Patients Daily)
Primary care clinics serving 5-10 patients daily represent ideal EHBT-75 deployment scenarios. The compact footprint fits seamlessly into clinic workflows without requiring dedicated laboratory space. Lower capital cost reduces financial barriers for independent practices and community health centers.
The clinical justification centers on diagnostic consolidation. Rather than collecting specimens for reference laboratory processing requiring 24-48 hours and incurring send-out fees, clinics perform immediate POC CBC assessment enabling same-day diagnostic decisions. Anemia presenting with fatigue receives immediate confirmation through POC hematocrit and hemoglobin. Suspected infections trigger rapid WBC and differential assessment guiding antibiotic selection. Capillary sampling eliminates pediatric and geriatric venipuncture challenges.
Facility impact studies demonstrate 20-30% laboratory cost reduction through elimination of reference laboratory send-outs, combined with improved clinical outcomes from rapid diagnostic turnaround. Patient satisfaction improves through same-day results and reduced appointment complexity.
Hospital Emergency Department (100+ Patients Daily)
Emergency departments managing 100+ patients daily warrant sophisticated deployment strategies combining EHBT-75 and EHBT-50 capabilities. Distributed EHBT-75 units strategically positioned throughout the emergency department enable rapid CBC screening at the point of care—supporting triage decisions, sepsis protocols, and acute hematologic assessment.
The 6-minute result turnaround proves transformative for sepsis management. Current sepsis protocols mandate antibiotic initiation within 1 hour of presentation; rapid POC CBC assessment identifying elevated WBC and left shift (immature neutrophils) enables immediate sepsis recognition and antimicrobial escalation, reducing door-to-antibiotic time from typical 45 minutes to under 15 minutes.
Central EHBT-50 placement enables comprehensive biomarker assessment consolidating cardiac markers, inflammatory markers, and metabolic parameters. Chest pain presentations receive rapid troponin assessment guiding admission decisions. Septic patients undergo concurrent CBC and inflammatory marker assessment (CRP, PCT) providing multi-dimensional infection confirmation.
Facility impact encompasses accelerated clinical decision-making, improved sepsis outcomes, reduced length of stay through faster diagnostic clarity, and emergency department throughput improvement from reduced waiting times for laboratory results.
Multi-Specialty Clinic (50+ Patients Daily)
Multi-specialty clinics managing 50+ diverse patient presentations benefit from EHBT-50 as the primary platform. Comprehensive testing consolidation enables infection workup combining CBC + immunoassay in single instrument. Diabetes management integrates glucose + HbA1c assessment. Thyroid dysfunction workup combines CBC + TSH + thyroid hormone measurement.
The operational impact proves substantial. Elimination of 3-4 separate devices (hematology analyzer, biochemistry analyzer, immunoassay analyzer, urinalysis system) recovers 60% of laboratory equipment footprint. Simplified maintenance protocols, reduced staff training requirements, and streamlined LIS integration generate 30-40% reduction in total operating costs. Same-day comprehensive results enable single-visit diagnostic confirmation, improving patient satisfaction and clinical efficiency.
Mobile Health Unit / Rural Clinic
Mobile health units and rural clinics operating under severe space and infrastructure constraints find the EHBT-75 ideally suited to their requirements. The compact footprint (415 × 203 × 483 mm) fits readily into mobile units designed for portability. Ultra-low power consumption (48VA) operates from standard electrical outlets or battery backup systems, enabling deployment in facilities with inconsistent power infrastructure.
Maintenance-free single-use cartridges stored at room temperature eliminate complex supply chains and cold storage requirements that challenge rural healthcare delivery. Capillary sampling eliminates venipuncture infrastructure requirements. Results connectivity via WiFi or Ethernet enables remote consultation with higher-tier facilities when needed.
The clinical impact transforms diagnostic accessibility for underserved populations. Decentralized diagnostics reduce patient wait times by 50% compared to reference laboratory routing, improving care equity and health outcomes in resource-limited settings.
POC Blood Analyzer: Advanced Capabilities and Abnormal Cell Detection
Modern POC analyzers transcend traditional five-part differential hematology through advanced parametric expansion and sophisticated morphologic analysis.
7-Differential Parameter Expansion
Traditional five-differential counting identifies five primary white blood cell types: neutrophils (NEU), lymphocytes (LYM), monocytes (MON), eosinophils (EOS), and basophils (BAS). This limited classification misses important clinical information regarding bone marrow function, infection severity, and hematologic malignancy indicators.
Advanced seven-differential analysis expands this framework through additional parameters. Immature neutrophils (NST) indicate acute infection or bone marrow stress. Abnormal granulocyte morphology (NSG/NSH) signals hematologic dysfunction. Reticulocytes (RET) demonstrate bone marrow regenerative capacity—critical for assessing recovery following chemotherapy or monitoring response to anemia therapies. Atypical lymphocytes (ALY) suggest viral infection or early malignant lymphoproliferation. Platelet aggregates (PAg) identify platelet dysfunction or preservation issues.
The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) represent derived parameters providing prognostic information regarding infection severity and inflammatory burden beyond traditional differential assessment.
Clinical Significance of Advanced Detection
NST detection transforms sepsis confirmation protocols. Immature neutrophil identification provides supporting evidenceof overwhelming infection, enabling rapid antibiotic escalation. Combined with inflammatory markers (CRP, PCT), immature neutrophil detection guides antimicrobial stewardship through objective microbial burden assessment.
Reticulocyte trends are useful for evaluating marrow erythroid recovery after chemotherapy. Rising RET counts suggest recovering erythropoiesis, whereas persistently low RET levels warrant closer monitoring and correlation with ANC, hemoglobin, and platelet recovery.
ALY morphology provides viral infection indication beyond simple lymphocytosis. Characteristic atypical lymphocyte appearance combined with elevated lymphocyte percentage suggests infectious mononucleosis, CMV infection, or acute viral hepatitis—enabling targeted diagnostic confirmation and counseling regarding activity restriction.
Elevated immature granulocytes (NSG/NSH) may reflect marrow stress from infection, inflammation, or growth factor therapy. When accompanied by cytopenias, circulating blasts, or persistent abnormalities, further evaluation with a peripheral smear and possibly hematology consultation is warranted.
Quality and Regulatory Standards
Healthcare procurement decisions require evidence-based confidence in analytical performance and regulatory compliance. Modern POC analyzers demonstrate rigorous quality standards meeting international requirements.
Accuracy and Performance Metrics
Laboratory-grade correlation coefficients demonstrate exceptional analytical accuracy. WBC measurements achieve 0.9962 correlation with reference laboratory values, RBC 0.9787, hemoglobin 0.9867, and platelets 0.9834. These correlation coefficients exceed typical acceptance criteria, ensuring clinical reliability for critical clinical decisions.
Independent validation studies confirm consistent performance across diverse patient populations and pathologic conditions. Abnormal samples with severe anemia, leukocytosis, or malignant morphology demonstrate maintained accuracy, enabling confident interpretation across the full pathologic spectrum.
Regulatory Approvals and Certifications
Both EHBT platforms carry CE Mark certification for European Union regulatory compliance, demonstrating meeting EU Medical Device Directive requirements. FDA clearance pathway (in process) ensures alignment with U.S. regulatory requirements. ISO 13485:2016 certification confirms manufacturing quality management system compliance. CLIA waiver eligibility (pending final determination) positions analyzers for clinical laboratory improvement amendments compliance in U.S. facilities.
Quality Control Systems
Dry-type QC card systems eliminate complex daily recalibration procedures required by traditional analyzers. Built-in automatic QC trending and alerts notify operators of potential systematic drift requiring corrective action. This streamlined quality control approach maintains analytical reliability while dramatically reducing operator burden and quality control failure risks.
Conclusione
POC blood analyzer selection represents a strategic healthcare decision with profound implications for clinical outcomes, operational efficiency, and financial performance. The distinction between dedicated hematology platforms like the EHBT-75 and comprehensive multi-functional systems like the EHBT-50 creates important tradeoffs requiring systematic evaluation against facility-specific requirements.
Dedicated hematology analyzers serve smaller volume settings, emergency departments, and resource-limited environments through cost efficiency, compact deployment, and focused CBC excellence. Multi-functional platforms consolidate laboratory testing into integrated platforms serving comprehensive diagnostic requirements with superior operational economics for larger facilities.
The most effective procurement approach avoids one-size-fits-all solutions. Instead, healthcare leaders should align analyzer selection with documented patient volume, required testing scope, available physical and financial infrastructure, and strategic clinical objectives. This evidence-based approach ensures analyzer deployment generates maximum value through optimized diagnostic turnaround, eliminated send-outs, consolidated laboratory platforms, and ultimately improved patient outcomes.
The rapid advancement in POC analyzer technology, exemplified by AI-driven morphologic analysis, single-use cartridge systems, and comprehensive parameter expansion, has democratized access to laboratory-grade diagnostics at the point of care. By leveraging these capabilities through thoughtful platform selection, healthcare facilities can transform diagnostic delivery, accelerate clinical decision-making, and enhance health outcomes across their patient populations.